The Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) conducted the 2024 Functional Literacy, Education, and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS), which aims to gather data as bases in determining the state of literacy in the country.
The 2024 FLEMMS adopts a revised operational definition and methodology for measuring basic and functional literacy as approved by the PSA Board through Resolution No. 13, Series of 2024.
Basic literacy is defined as the ability of a person to read and write a simple message in any language or dialect with understanding, and to compute or perform basic mathematical operations.
Functional literacy is the ability of a person to read, write, compute and comprehend. In addition to the basic literacy skills, functional literacy includes higher level of comprehension skills, such as integrating two or more pieces of information and making inferences based on the given information.
Basic literacy rate is computed for individuals 5 years old and over, while functional literacy rate is computed for individuals 10 to 64 years old.
17 in 20 persons aged 5 years and over in Eastern Visayas had basic literacy
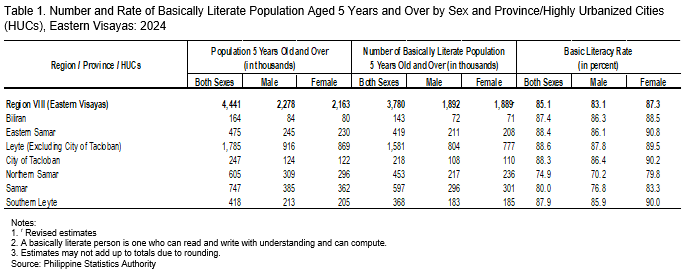
The 2024 FLEMMS results showed that 85.1 percent, or approximately 17 out of every 20 persons aged 5 years and over in Eastern Visayas, had basic literacy. This corresponds to around 3.78 million individuals who can read, write, and compute, out of the estimated 4.44 million individuals in the same age group (Table 1).
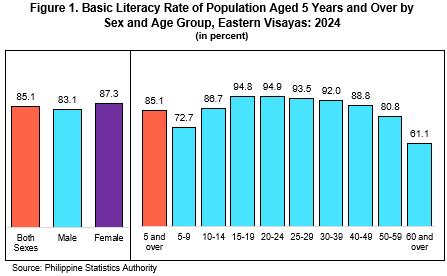
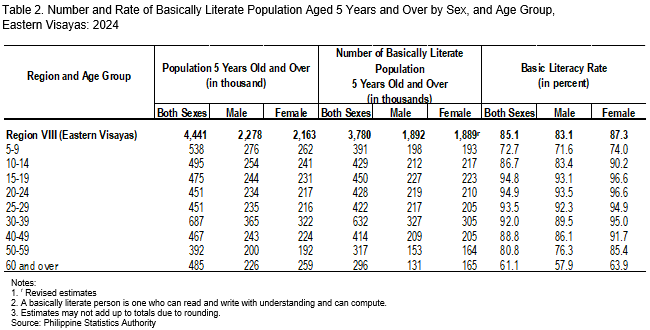
In terms of sex, the basic literacy rate among the population aged 5 years and over was higher among females at 87.3 percent than males at 83.1 percent (Figure 1 and Table 1). By age group, individuals aged 20 to 24 years registered the highest basic literacy rate at 94.9 percent, while the lowest was recorded among those aged 60 years and over at 61.1 percent (Figure 1 and Table 2).
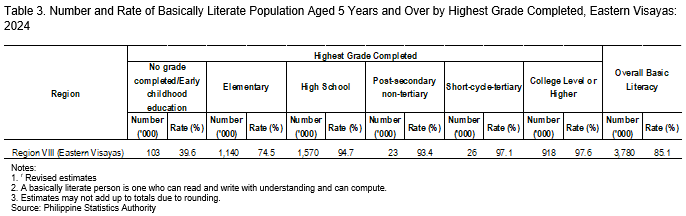
In terms of highest grade completed, individuals who attained college level or higher recorded the highest basic literacy rate at 97.6 percent. Conversely, those with no grade completed or who have only completed early childhood education exhibited the lowest basic literacy rate at 39.6 percent (Table 3).

Basic literacy rates among the population aged 5 years and over varied across provinces in the region. Leyte (excluding Tacloban City) recorded the highest basic literacy rate at 88.6 percent, while Northern Samar registered the lowest at 74.9 percent. Meanwhile, the lone Highly Urbanized City (HUC) of Tacloban posted a basic literacy rate of 88.3 percent (Figure 2 and Table 1).
1 in 9 persons aged 5 years and over in Eastern Visayas were illiterate
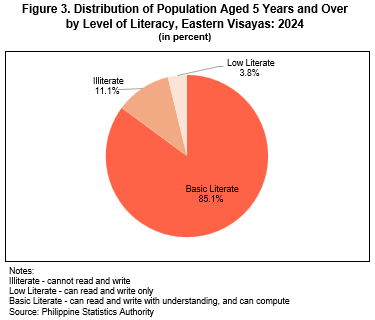
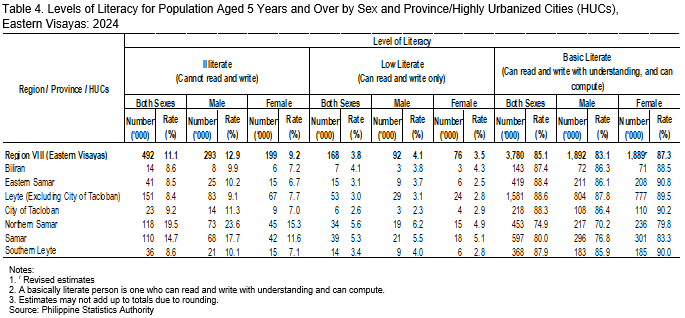
Among individuals aged 5 years and over in Eastern Visayas, 11.1 percent, or approximately 1 in every 9 persons, were unable to read and write and are therefore classified as illiterate. The proportion of illiterate individuals was higher among males (12.9%) compared with females (9.2%). Across provinces, Northern Samar recorded the highest proportion of illiterate individuals aged 5 years and over at 19.5 percent. Meanwhile, 9.2 percent of the population aged 5 years and over in Tacloban City were classified as illiterate (Figure 3 and Table 4).
About 3 out of 5 persons aged 10 to 64 years in Eastern Visayas were functionally literate
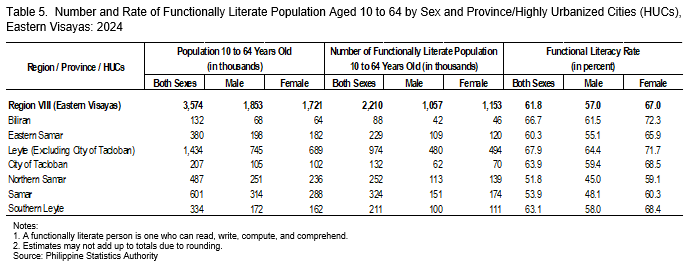
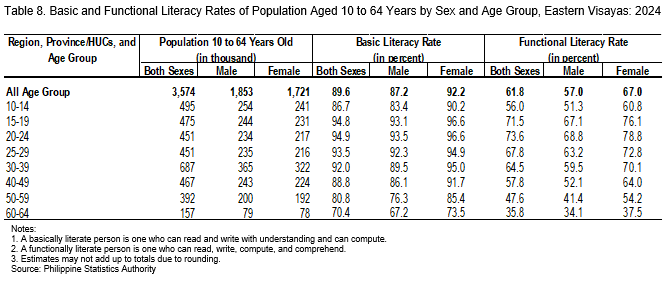
In 2024, the functional literacy rate in Eastern Visayas was recorded at 61.8 percent, indicating that approximately 3 out of every 5 individuals aged 10 to 64 years were functionally literate. This translates to about 2.21 million individuals who possess the ability to read, write, compute, and comprehend, out of the estimated 3.57 million individuals in the same age group (Table 5).
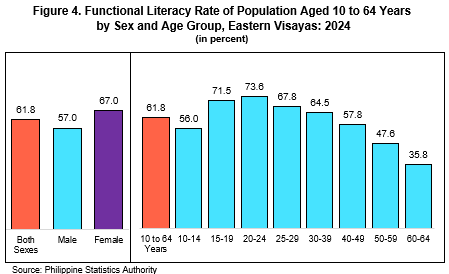
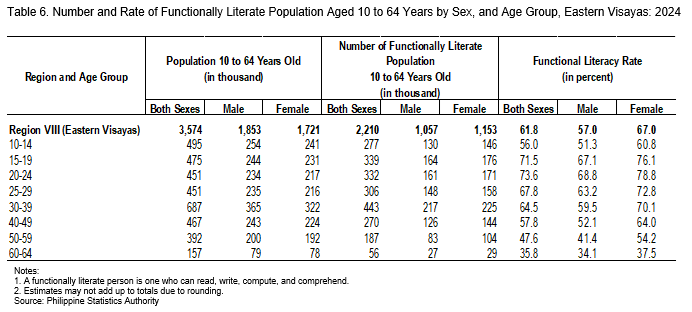
By sex, females registered a higher functional literacy rate at 67.0 percent, compared with 57.0 percent among males (Figure 4 and Table 5). Across age groups, individuals aged 20 to 24 years recorded the highest functional literacy rate at 73.6 percent, while those aged 60 to 64 years posted the lowest at 35.8 percent (Figure 4 and Table 6).
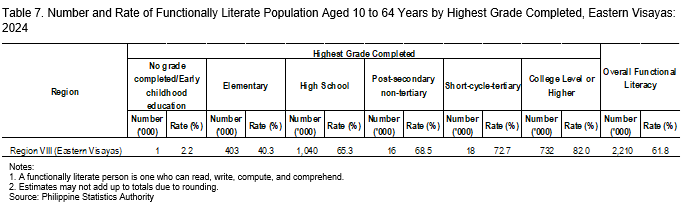
In terms of highest grade completed, individuals who attained college level or higher recorded the highest functional literacy rate at 82.0 percent. Conversely, those with no grade completed or only completed early childhood education had the lowest functional literacy rate at 2.2 percent (Table 7).
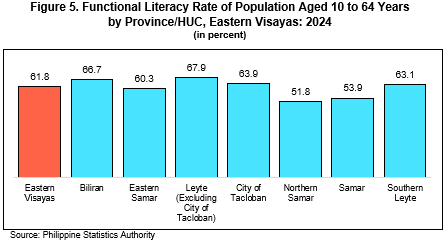
Among the provinces, Leyte (excluding Tacloban City) recorded the highest functional literacy rate at 67.9 percent, while Northern Samar registered the lowest at 51.8 percent. Meanwhile, the functional literacy rate in Tacloban City was estimated at 63.9 percent (Table 5).
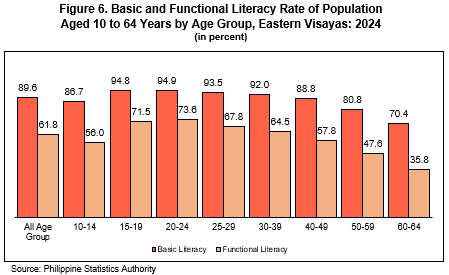
The gap between basic literacy and functional literacy in Eastern Visayas was highest in the age group 60 to 64 years
Among individuals aged 10 to 64 years in Eastern Visayas, 89.6 percent were basic literate, while only 61.8 percent were functionally literate, revealing a gap of 27.8 percentage points. This means that for every ten individuals aged 10 to 64 who can read, write, and compute, nearly three (3) have difficulty with comprehension.
The gap between basic literacy and functional literacy was highest among individuals aged 60 to 64 years. This indicates that for every three (3) individuals who can read, write, and compute, approximately one (1) experiences difficulty with comprehension (Figure 6 and Table 8).
TECHNICAL NOTES
A. Background of the Survey
The Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS) is a household-based nationwide survey conducted every five (5) years in accordance with the Designation of Statistical Activities that will Generate Critical Data for Decision-making of the Government and the Private Sector (Executive Order No. 352 of 1996). The 2024 FLEMMS is the seventh in the series of literacy surveys in the country starting in 1989. Prior to this survey round, FLEMMS was conducted in 2019.
The 2024 FLEMMS adopted the revised operational definition and methodology in estimating basic and functional literacy in the Philippines as approved by the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) Board through Resolution No. 13, Series of 2024.
Also, for the first time, the 2024 FLEMMS utilized the Computer-Assisted Personal Interviewing (CAPI) System for the collection of the FLEMMS Form 1 (Household Questionnaire) and FLEMMS Form 3 (Individual Questionnaire).
Furthermore, the 2024 FLEMMS added new data items that are aligned with the Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies (PIAAC), which is the recommended tool to measure functional literacy endorsed by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
B. Scope and Coverage
The reporting unit is the household, which means that the statistics emanating from this survey will refer to the characteristics of the population residing in private households. Persons who reside in the institutions are not within the scope of the survey.
With the province/HUC as domain, the survey operations for 2024 FLEMMS ran from September to October 2024 which covered 179,560 eligible sample households and 610,590 individuals/household members five (5) years old and over, respectively.
C. Revised Operational Definitions and Methodology
1. Basic Literacy
Conceptual definition - the ability of a person to read, write, and compute with understanding a simple message in any language or dialect and be able to perform basic mathematical operations.
Operational definition - the ability to read, write, and compute (with numerical skill)
2. Functional Literacy
Conceptual definition - is a significantly higher level of literacy which includes reading, writing, numeracy, and comprehension skills. The skills must be sufficiently advanced to enable the individual to engage fully and efficiently in activities commonly occurring in this life situation that require a reasonable capability of communicating by written language.
Operational Definition - the ability to read, write, compute, and comprehend (with numerical and comprehension skill)
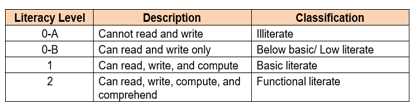
3. Levels of Literacy - identifies the range of skills and competencies of an individual. Specifically,
SGD. WILMA A. PERANTE
Regional Director

