
The total fishery production in Biliran reached 1,750.10 metric tons (MT) during the fourth quarter of 2020. This figure is lower by 1.45 percent compared to the 1,775.87 MT during the same quarter of 2019. This can be attributed to the decrease in the municipal fishery and aquaculture sector (Refer to Table 1).
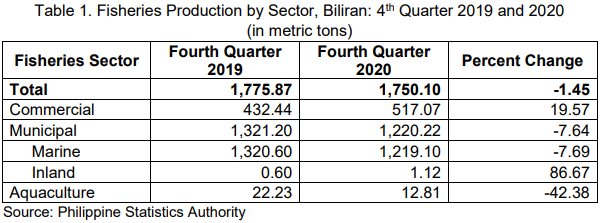
By sector, the municipal fishery sector accounted for the largest share (69.72%) to the total fishery production in the province during the fourth quarter of 2020. Commercial fishery and aquaculture accounted for 29.55 percent and 0.73 percent, respectively.
COMMERCIAL FISHERY
Commercial fishery production reached 517.07 MT during the fourth quarter of 2020 which is 19.57 percent higher compared to its production of 432.44 MT during the fourth quarter of 2019. This can be traced to good weather condition observed during the reference quarter that enabled more fishing trips.

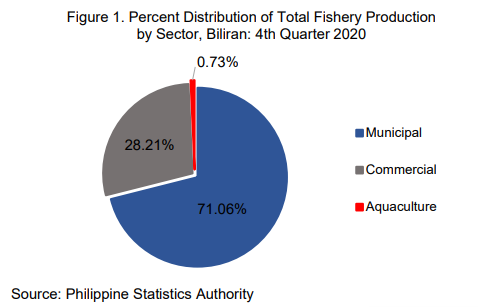
Among the commercial fishes caught during the fourth quarter of 2020, Bali sardinella had the biggest production at 122.88 MT (23.76%). Roundscad came in next with a production of 114.58 MT (22.16%), followed by Frigate tuna with 65.23 MT (12.62%), Indo-pacific mackerel with 57.75 MT (11.17%), and Crevalle with 34.17 MT (6.61%).
MUNICIPAL FISHERY
The Province recorded a total municipal fishery production of 1,220.22 MT. This posted a decline of 7.64 percent compared with its reported production of 1,321.20 MT during the same quarter of 2019.
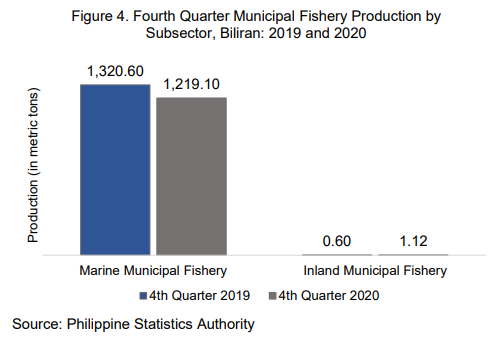
By subsector, marine municipal accounted for almost all (99.91%) of the total municipal fishery production in the fourth quarter of 2020. Its production, however, decreased by 7.69 percent, from 1,320.60 MT to 1,219.10 MT.
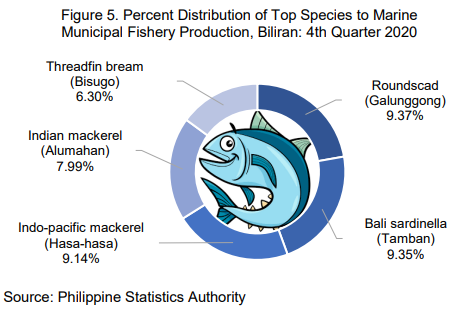
The top five catch for the marine municipal fishery during the fourth quarter of 2020 were Roundscad with 114.20 MT (9.37%), Bali sardinella with 113.97 MT (9.35%), Indo-pacific mackerel with 111.43 MT (9.14%), Indian mackerel with 97.35 MT (7.99%), and Threadfin bream with 76.79 MT (6.30%).
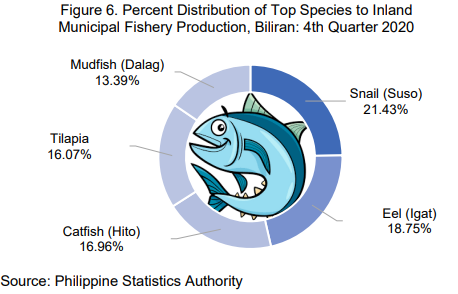
Inland fishery production, on the other hand, shared 0.09 percent to the total municipal fishery production during the fourth quarter of 2020. Its production increased by 86.67 percent, from 0.60 MT to 1.12 MT.
AQUACULTURE FISHERY
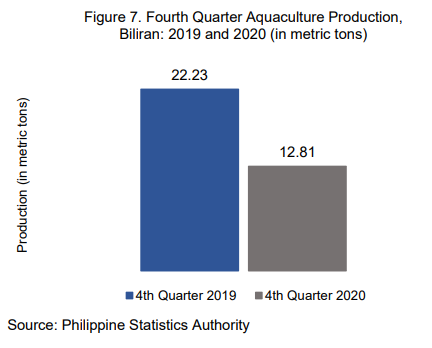
Aquaculture fishery contributed the least to the total provincial fishery production among the three fishery sectors. Its production was recorded at 12.81 MT during the fourth quarter of 2020, lower by 42.38 percent compared to its production of 22.23 MT during the same quarter of 2019.
The catch for this sector were milkfish from brackishwater fishponds and marine cages with a total production of 12.72 MT (99.30%) and tilapia from freshwater fishponds with a production of 0.09 MT (0.70%).
TECHNICAL NOTES
The Fisheries Production Survey of the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) is divided into four (4) major fisheries surveys. These are the Quarterly Commercial Fisheries Survey (QCFS), Quarterly Municipal Fisheries Survey (QMFS), Quarterly Inland Fisheries Survey (QIFS) and Quarterly Aquaculture Survey (QAqS). The commercial and municipal fisheries surveys aim to provide quarterly data on volume and value of fish production by species, by region and by province. The aquaculture surveys are intended to generate quarterly data on volume and value of cultured species by environment, type of aquafarm, region and province.
The survey on commercial fisheries production covered 57 provinces and cities. For municipal fisheries and aquaculture surveys, over 81 provinces and cities were covered. The sampling frames for the surveys of commercial and municipal fisheries were established in 2000 through a nationwide listing of landing centers (LCs). Updating of the lists was conducted over the years. The design used was a two-stage stratified random sampling with the landing centers as the first-stage sampling units and the fishing boats as the second stage sampling units. The landing centers were stratified based on volume of fish unloaded. The province was the domain of the survey. Inland municipal fisheries included fishing in inland waters such as lakes, rivers, dams, marshes, swamps, etc. Household engaged in inland fishing was the unit of enumeration. For aquaculture survey, the lists of brackishwater fishponds, freshwater fishponds, freshwater fish pens/fish cages, marine fish pens/fish cages, oyster/mussel and seaweed farms by province served as the sampling frames.
Updating of list frames for aquaculture was done simultaneously with the landing center during the previous years.
Concepts and Definitions:
Aquaculture – fishery operation involving all forms of raising and culturing of fish and other fishery species in marine, brackish and fresh water environment. Examples are fishponds, fish pens, fish cages, mussel, oyster, seaweed farms and hatcheries.
Aquafarm – the farming facilities used in the culture or propagation of aquatic species including fish, mollusk, crustaceans and aquatic plants for purposes of rearing to enhance production.
Brackish water – mixture of seawater and freshwater with salinity that varies with the tide. Examples are estuaries, mangroves and mouths of rivers where seawater enters during high tide.
Fisheries – all activities relating to the act or business of fishing, culturing, preserving, processing, marketing, developing, conserving and managing aquatic resources and the fishery areas including the privilege to fish or take aquatic resources thereof (RA 8550).
Fisheries Sector – the sector engaged in the production, growing, harvesting, processing, marketing, developing, conserving and managing of aquatic resources and fishing areas.
Fish Cage – stationary or floating fish enclosure made of synthetic net wire/bamboo screen or other materials set in the form of inverted mosquito net (“hapa” type) with or without cover with all sides either tied to poles staked to the water bottom or with anchored floats for aquaculture purposes.
Fishing Gear – any instrument or device and its accessories utilized in taking fish and other fishery species.
Fishing Grounds – areas in any body of water where fish and other aquatic resources congregate and become target of capture. Fish Pen – an artificial enclosure constructed within a body of water for culturing fish and fishery/aquatic resources made up of bamboo poles closely arranged in an enclosure with wooden materials, screen or nylon netting to prevent escape of fish.
Fishpond – a body of water (artificial or natural) where fish and other aquatic products are cultured, raised or cultivated under controlled conditions. This is a landbased type of aquafarm. Note that the setting-up of fish cages in ponds does not make the operation of fish cage and at the same time a fishpond.
Freshwater – water without salt or marine origin, such as generally found in lakes, rivers, canals, dams, reservoirs, paddy fields and swamps.
Inland Municipal Fishing – the catching of fish, crustaceans, mollusks and all other aquatic animals and plants in inland water like lakes, rivers, dams, marshes, etc. using simple gears and fishing boats some of which are non-motorized with a capacity of three (3) gross tons or less; or fishing not requiring the use of fishing boats.
Landing Center – place where the fish catch and other aquatic products are unloaded and traded.
Municipal Fishing – covers fishing operation carried out with or without the use of a boat weighing three (3) gross tons or less.

